BC 2000
Minoans and Greeks discover that the plant silphium is an effective oral contraceptive, but it proves so popular that it is harvested to extinction.
1832
American physician Charles Knowlton publishes Fruits of Philosophy. The first book on contraception.
1914
American activist and nurse Margaret Sanger coins the term “birth control.”
1918
African American women of the Women’s Political Association of Harlem hold their first public lecture on birth control.

1921
Sanger returns to the U.S. and establishes the American Birth Control League and opens the nation’s first birth control clinic in Brooklyn, NY.
Austrian physician Ludwig Haberlandt understands the potential for developing a hormonal contraceptive pill, but is maligned by his peers.
1928-1929
American scientists identify the role of the human sex hormones estrogen and progesterone in fertility and pregnancy.
1933
American chemist Russell Marker synthetizes progesterone from yams.
Sanger persuades endocrinologist Gregory Pincus to work on a birth control pill. At the time, 30 states restrict the sale of contraceptives.
Catholic obstetrician-gynecologist John Rock joins the team. Women’s rights activist and heiress Katherine McCormick funds the mission.
Early clinical trials determine that the birth control pill is 100% effective. While effective, early formulations of oral contraception contained high doses of hormones. Today, The Pill delivers 99% efficacy when used as directed, yet contains only a fraction of the hormones used initially.
The FDA approves the pill, but only for severe menstrual disorders, not as a contraceptive. Many women begin to report severe menstrual disorders.
1960
The first oral contraceptive, a mix of progesterone and estrogen, is approved by the FDA. It quickly becomes known as “The Pill.”
1962
In the U.S., 1.2 million women are prescribed The Pill; that figure doubles a year later.
1965
U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Griswold v. Connecticut legalizes birth control for married couples.
The Pill becomes most popular form of birth control in the U.S. with over 6 million women taking it.

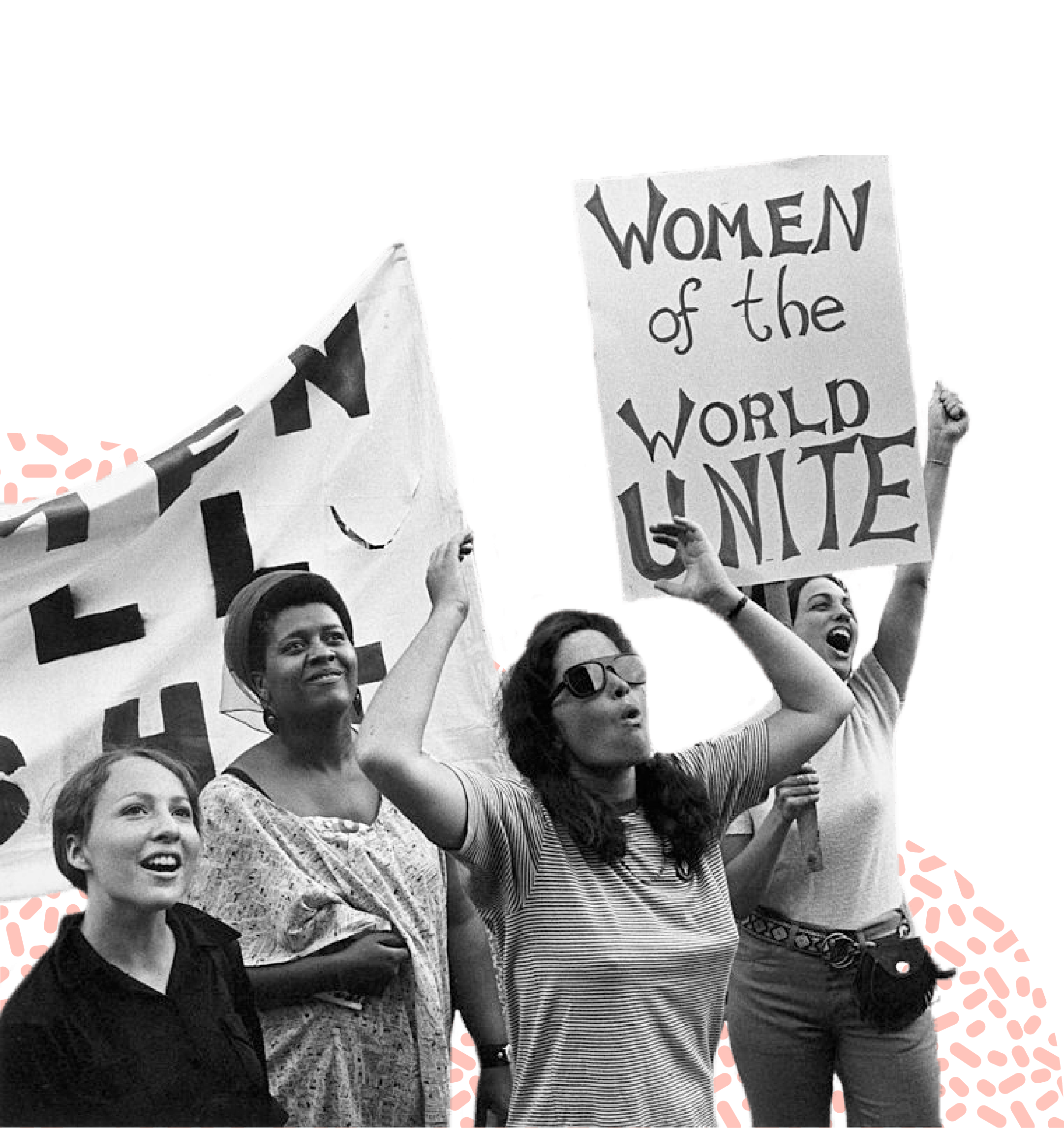
1968-1970
American author and civil rights activist Toni Cade Bambara publishes an essay calling attention to controversies surrounding contraception in communities of color.
1972
A landmark U.S. Supreme Court ruling (Eisenstadt v. Baird) legalizes birth control for unmarried people.
1977
The FDA approves Ortho Pharmaceutical’s Tri-Cyclen pill as treatment for acne.
Erickson v. Bartell, a Federal case ruling states that employer’s insurance plans (companies with 15 or more employees) cannot exclude prescription contraception if the plan covers other drugs and medical devices.
FDA approves OTC status for emergency contraception (Plan B One-Step) for consumers age 18 and older.
A British study of 23,000 women using The Pill and 23,000 controls, followed for up to 39 years, demonstrates the health benefits of The Pill, including halving the life-time risk of ovarian cancer & uterine cancer, and reducing the risk of colorectal cancer and melanomas, iron deficiency anemia and pelvic inflammatory disease.
The Affordable Care Act requires preventative health care to include coverage of all FDA approved forms of contraception.
2012
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that the Pill should be available over-the-counter (other major medical organizations later affirmed this recommendation).
2013
FDA approves emergency contraception (Plan B One-Step) for unrestricted sale on the shelf.
2014
The U.S. Supreme Court rules that employers with religious objections may refuse to cover contraception in employee health insurance plans.


2016
Cadence Health, a mission-driven organization focused on women’s health, acquires the rights to two of the most popular oral contraceptives, Lo/Ovral and Alesse from a leading pharmaceutical company. With this acquisition, Cadence Health begins the journey to bring The Pill Over-the-Counter.
2019
With an estimated 50 to 80 million women around the world using The Pill safely and effectively to prevent unintended pregnancy, Cadence Health embarks on a bold plan to improve access to birth control pills by making them available over-the-counter.

